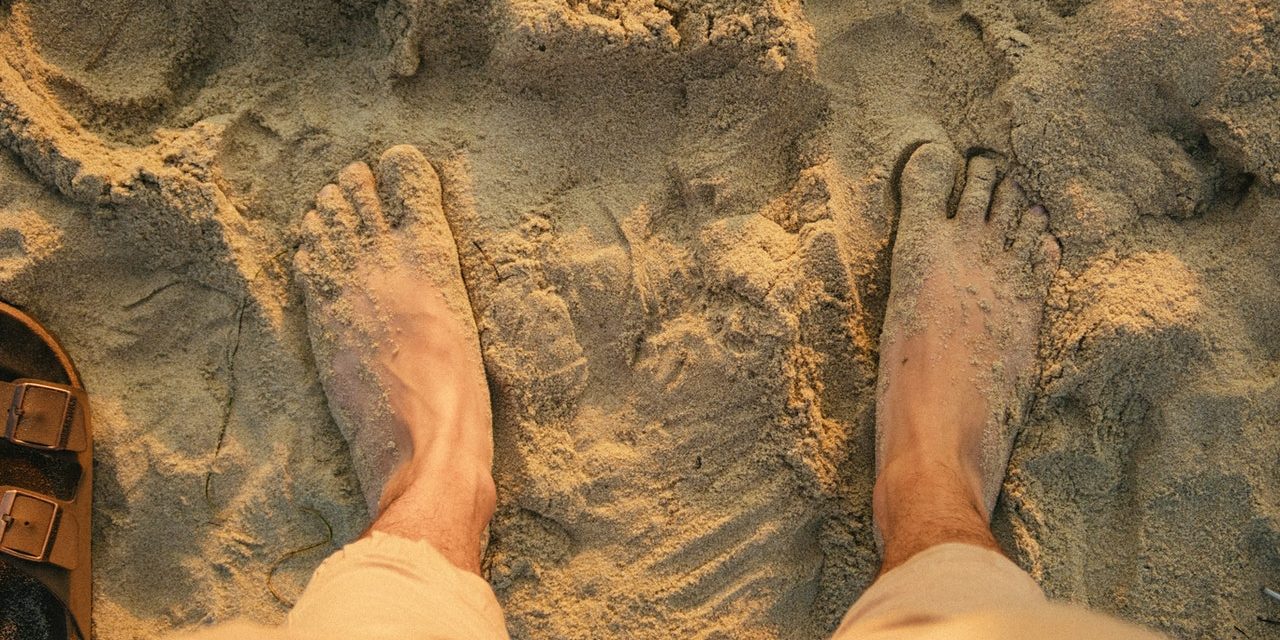
Henna, derived from the Lawsonia inermis plant, possesses several properties that are believed to have anti-fungal effects. Here are some of the potential anti-fungal properties of henna:
1. Antimicrobial Activity: Henna has been found to exhibit antimicrobial properties against various microorganisms, including fungi. Studies have shown that henna extracts and compounds derived from henna, such as lawsone, have inhibitory effects on the growth of fungal species.
2. Fungicidal Action: Henna has been reported to have fungicidal properties, meaning it can actively kill or inhibit the growth of fungi. It has demonstrated effectiveness against common fungal pathogens, including Candida species, Aspergillus species, and dermatophytes that cause skin infections.
3. Anti-inflammatory Effects: Henna possesses anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation associated with fungal infections. By reducing inflammation, henna may aid in alleviating the discomfort and symptoms caused by fungal overgrowth.
4. Astringent Properties: Henna has astringent properties that can help dry out and tighten the skin, creating an unfavorable environment for fungal growth. This property can be beneficial in managing conditions like athlete’s foot or other fungal infections of the skin.
5. Moisture Absorption: Henna has the ability to absorb moisture from the skin or affected area. This moisture-absorbing property can help create a less favorable environment for fungal growth, as fungi thrive in warm and moist conditions.
It’s important to note that while henna may possess potential anti-fungal properties, it should not be considered a standalone treatment for fungal infections. If you suspect or have been diagnosed with a fungal infection, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist for appropriate diagnosis and treatment. They can provide specific antifungal medications or therapies tailored to your condition.